Convex Optimization Note(2): Convex Function
中文版笔记感觉这个博主总结的比较清楚
1. Convex Function
Convex can also be used to describe the feature of a function.
Definition: \[f(\theta x+(1-\theta) y)\leq\theta f(x) + (1-\theta)f(y)\]
Conditions:
First Order: \(f(x) + \nabla f(x)^T(y-x)\leq f(y)\)
Second Order: \(\nabla^2f\succeq0\) (positive semi-definite Hessian Matrix)
Semi-definite: \(\nabla^2f(x)\succeq0\) means that \(\forall y\in\mathbb{R}^n\), \(y^T\nabla^2f(x)y\geq0\)
Examples:
Norm: Any norm \(f(x):\mathbb{R}^n\rightarrow\mathbb{R}\) is covex
Max: max function is convex
Geometric Mean: \(f(x)=(\prod_{i=1}^nx_i)^{1/n}\) concave, prove by second-order condition
Sublevel/Superlevel Sets
Definition: \[C_{\alpha}=\{x\in\textbf{dom }f|f(x)\leq\alpha\}\] Property: All sublevel sets of convex function are convex sets(converse not).
It is said to be a good way to construct convex sets.
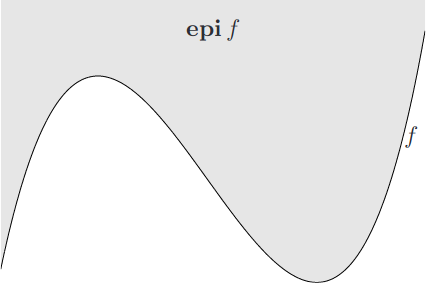
Epigraph
Epi means "above" so epigraph basically means area above the function. We should notice that the epigraph actually expands the dimension of the original function. That is, if \(f:\mathbb{R}^n\rightarrow\mathbb{R}\), then \(\textbf{epi }f\subset\mathbb{R}^{n+1}\).
Definition: \[\textbf{epi }f=\{(x,t)|f(x)\leq t, x\in\textbf{dom }f\}\]
Jensen's inequality
Convex Combination for more than 2 points: \[f(\theta_1 x_1+\dots \theta_kx_k)\leq\theta_1f(x_1)+\dots \theta_kf(x_k)\] It can be further proved about expectation: \[f(\mathbb{E}(x))\leq\mathbb{E}(f(x))\]
2. Operations pereserve Convexity
Non-negative weighted sum
Affine mapping \(g(x)=f(Ax+b)\)
Maximum \(f(x)=\max\{f_1(x)+f_2(x)\}\)
It can further be prove that \(f(x)=\sup_{y\in A}||x-y||\) is convex.(furthest distance from a set)
Almost every convex function can be represented as the supremum of a family of affine functions.
Composition \(f(x)=g(h(x))\), not necessarily convex, look at the expression of \(f''(x)\)
Minimization: \(f(x)=\inf_{y\in A}f(x,y)\) is convex if \(f(x,y)\) is convex and \(A\) is convex set(Additional requirement on convexity of \(A\)).
Perspective: \(f(x)=t\cdot f(x/t)\) is convex if \(f(x)\) is convex and \(t>0\).
Conjugate function: \(f^*(y)=\sup_{x\in\textbf{dom}}(y^ Tx-f(x))\) is convex regardless of the convexity of \(f(x)\).
The maximum distance between \(f(x)\) and line \(y=x\):
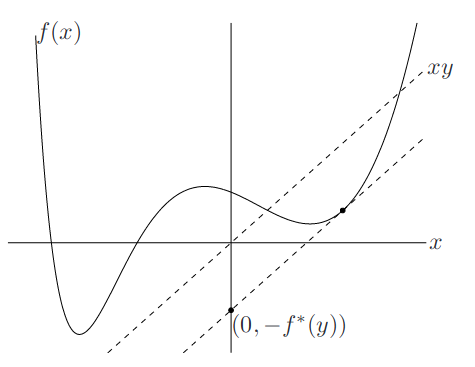
3. Quasiconvex Function
Definition: If all sublevel sets of \(f(x)\) are convex, then \(f(x)\) is quasiconvex. One example of a set
that is quasi-convex but not convex: 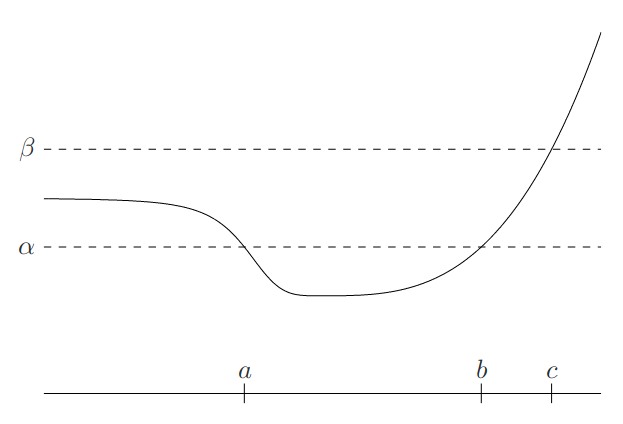
Property:
- \(f(\theta x_1+(1-\theta)x_2)\leq \max\{f(x_1),f(x_2)\}\)
Conditions:
First Order: \(f(y)<f(x)\implies\nabla f(x)^T(y-x)\leq 0\)
Second Order: \(\forall y\in R^n\), \(y^T\nabla f(x)\implies\) \(y^T\nabla^2f(x)y\succeq 0\)
4. Log-Concave Function and Log-Convex Function
Definition: Log-Concave: \(f(x)\) is log-concave if \(\log f(x)\) is concave. \[f(\theta x_1+(1-\theta)x_2)\geq f(x_1)^{\theta}f(x_2)^{1-\theta}\]